In the world of wireless communication, it is important for everyone to understand the ins and outs of antenna technology. This guide is here to help you understand dual polarization antennas, a crucial piece that plays a big role in how well modern communication systems work.
In today’s fast-moving tech world, it’s important to know how dual polarization antennas work and why they matter. These antennas are leading the charge in improving communication systems, promising better signal quality and more efficient use of bandwidth.
A dual polarization antenna is a device that excels in transmitting and receiving signals in two distinct polarization planes—typically horizontal and vertical. This dual capability allows for doubling the capacity of a communication system without the need for additional bandwidth or increased transmitting power, making it a cornerstone of efficient communication.
But what sets this technology apart, and why is it increasingly adopted across various sectors?
The Historical Background of Antenna Polarization
To truly appreciate dual polarization antennas, it helps to take a quick look at their origins. The story begins in the 19th century with the pioneering work of James Clerk Maxwell. Maxwell’s equations fundamentally changed how we understand electromagnetic waves, laying the groundwork for all modern wireless communication—including how antennas manage polarization.
Later, in the late 1880s, Heinrich Hertz took theory into practice. Using simple dipole antennas, Hertz was the first to demonstrate polarization experimentally, confirming Maxwell’s predictions about electromagnetic wave behavior. These foundational breakthroughs opened the door to the sophisticated antenna designs and signal-handling techniques we benefit from today.
What is Dual Polarity?
In simple terms, dual polarity means that an antenna can transmit and receive signals in two different directions simultaneously. This is achieved by using two sets of elements or antennas that are positioned at right angles to each other. The two sets of elements are designed to transmit and receive signals in two orthogonal planes, typically horizontal and vertical.

The use of dual polarity antennas offers several advantages. Firstly, it improves the system’s resistance to interference. By transmitting and receiving signals in two different planes, the antenna can better reject signals coming from unwanted directions. This helps to reduce the impact of interference and improves the overall signal quality.
Secondly, dual polarity antennas enhance signal diversity. By transmitting and receiving signals in two different directions, the antenna can capture and utilize signals that may arrive at different angles or paths. This is particularly useful in environments where there are obstructions or multipath propagation, where signals can take multiple paths and arrive at the receiver with different delays and phases. By utilizing the signals from both polarities, the antenna can improve the overall signal strength and reliability.
In summary, dual polarity antennas provide improved interference rejection and signal diversity, which are crucial for maintaining reliable communications in diverse environments.
How Do Dual-Polarized Antennas Work?
Dual-polarized antennas work by transmitting and receiving signals in two different polarizations simultaneously. Polarization refers to the orientation of the electromagnetic waves as they are propagated through space.
In a single-polarized antenna, the electromagnetic waves are propagated in only one polarization, either horizontal or vertical. However, in a dual-polarized antenna, the waves are propagated in two orthogonal polarizations, typically horizontal and vertical.

To achieve this, dual-polarized antennas have two sets of radiating elements, each oriented in a different polarization. These radiating elements are typically arranged in a cross-polarized configuration, with one set of elements aligned horizontally and the other set aligned vertically.

When transmitting, the dual-polarized antenna can simultaneously emit signals in both horizontal and vertical polarizations. This allows for the transmission of two independent data streams over the same frequency band. Similarly, when receiving, the antenna can receive signals in both polarizations simultaneously, effectively doubling the received data.
The advantage of dual-polarized antennas is that they can transmit and receive more data over the same frequency band, effectively doubling the throughput of a communication channel. This makes them highly efficient in crowded spectrums where maximizing data transmission is critical.
Dual-polarized antennas are commonly used in various wireless communication systems such as point-to-point microwave links, cellular base stations, Wi-Fi networks, and satellite communication systems. They are particularly useful in scenarios where high data rates and efficient spectrum utilization are required.
How is Polarization Diversity Used in MIMO Systems?
Polarization diversity is a technique that leverages multiple polarizations—such as vertical and horizontal—within a single antenna system to improve communication reliability and efficiency. In MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) systems, this means using antennas that can transmit and receive signals in more than one polarization at the same time.

By doing so, polarization diversity tackles one of the persistent challenges in wireless communication: polarization mismatch. When signals reflect off buildings, trees, or other obstacles, their polarity can shift, leading to signal loss or degradation. A MIMO system equipped with dual-polarized antennas can capture these signals regardless of how their polarization changes along the path.
Another advantage is reduced multipath interference. With multiple polarizations available, the system can differentiate between direct signals and those arriving via reflections, helping to filter out interference and enhance clarity.
Practically, this approach allows MIMO systems to use fewer separate antennas while still transmitting and receiving multiple data streams. The use of orthogonal polarizations ensures the different streams don’t interfere with each other, keeping the signals distinct. This makes antenna arrays in cellular base stations and wireless backhaul links more compact and efficient.
However, while implementing polarization diversity can significantly improve performance and data rates, it may require more sophisticated—and sometimes pricier—antenna hardware. Despite the additional investment, the boost in throughput and spectral efficiency often makes it a valuable tool in modern high-capacity wireless networks.
What is a dual polarization antenna used for?
A dual polarization antenna is used for transmitting and receiving signals with two different polarizations simultaneously. It allows for the transmission and reception of two separate signals or two separate data streams on the same frequency band. This type of antenna is commonly used in wireless communication systems to increase the capacity and efficiency of the system by allowing the simultaneous transmission and reception of multiple signals. It is also used in radar systems to separate the reflected signals from different objects based on their polarization.

What are the Benefits of Dual-Polarization?
Dual-polarization offers several benefits in various applications. Some of the key benefits include:
1. Improved data quality: Dual-polarization provides more information about the target or scene being observed. By transmitting and receiving signals in both horizontal and vertical polarizations, it is possible to gather more detailed data about the target, resulting in higher-quality images and measurements.

2. Enhanced target discrimination: Dual-polarization allows for better discrimination between different types of targets. For example, in weather radar applications, it can help distinguish between rain, snow, hail, and other precipitation types. In remote sensing, it can aid in differentiating between various land cover types, such as forests, crops, and urban areas.
3. Increased sensitivity: Dual-polarization can enhance the sensitivity of radar systems. By transmitting and receiving signals in two polarizations, the radar can capture more of the backscattered energy from the target, leading to improved detection and measurement capabilities.
4. Reduced interference and clutter: Dual-polarization can help mitigate interference and clutter in radar systems. By using both polarizations, it is possible to separate the desired signal from unwanted signals and background noise, resulting in cleaner and more accurate measurements.
5. Improved performance in adverse weather conditions: Dual-polarization provides better performance in adverse weather conditions, such as heavy rain or snow. By utilizing both polarizations, it is possible to minimize the impact of signal attenuation and improve the accuracy of measurements.
6. Enhanced target recognition and classification: Dual-polarization can aid in target recognition and classification tasks. By analyzing the polarization properties of the backscattered signals, it is possible to identify and classify different types of targets based on their scattering characteristics.
Overall, dual-polarization offers significant advantages in terms of data quality, target discrimination, sensitivity, interference reduction, performance in adverse weather, and target recognition, making it a valuable tool in various applications such as weather radar, remote sensing, and military surveillance.
What emerging applications rely on advancements in antenna polarization?
Advancements in antenna polarization, particularly with the rise of adaptive and intelligent polarization technologies, are opening the door to a host of emerging applications.
Some notable areas leveraging these developments include:
Internet of Things (IoT): Modern IoT devices, from smart meters to environmental sensors, increasingly depend on robust wireless links that benefit from polarization diversity. This helps maintain reliable communication in dense urban environments packed with interfering signals.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and Drones: Reliable, high-throughput communication is essential for drone operations—especially when navigating complex terrain or urban canyons. Adaptive polarization enables more resilient drone-to-ground and drone-to-drone links, even as signal environments shift rapidly in flight.

Connected and Autonomous Vehicles: Next-generation vehicles are equipped with an array of wireless sensors and communication modules. Polarization advancements allow these systems to exchange data more efficiently, supporting applications like collision avoidance, automated navigation, real-time mapping, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication.
Smart Cities: From public Wi-Fi networks to sensor-powered infrastructure and emergency response systems, smart city initiatives benefit from antennas that can adapt polarization in response to changing conditions, ensuring consistent coverage and reliability for critical services.
Machine Learning Enhanced Networks: Recent research is exploring the integration of machine learning with wireless systems to dynamically optimize polarization—improving signal quality and network capacity on the fly as demands evolve.

Next-Generation Cellular Networks (5G and Beyond): As 5G and 6G technologies continue to roll out, polarization techniques play a key role in supporting higher data rates, lower latency, and greater network efficiency. Features such as intelligent reflective surfaces further enhance wireless performance, paving the way for innovative applications and services.
These advancements are not just theoretical—they are rapidly becoming essential for enabling the ever-growing ecosystem of connected devices and applications that define modern communication landscapes.
Why Use Dual-Polarized Antennas?
Dual-polarized antennas have the ability to transmit and receive data simultaneously on two different polarizations (horizontal and vertical). This allows for twice the amount of data to be transmitted at the same time, effectively doubling the capacity of the network.

Here are some reasons why dual-polarized antennas are beneficial:
1. Increased capacity: Dual-polarized antennas allow for more data to be transmitted at the same time, increasing the overall capacity of the network. This is especially important in high-density areas where multiple users are accessing the network simultaneously.
2. Improved signal quality: By transmitting and receiving data on two different polarizations, dual-polarized antennas can mitigate the effects of interference and multipath fading. This leads to improved signal quality and less packet loss, resulting in a more reliable and stable connection.
3. Better spectrum utilization: With the ability to transmit and receive data on two different polarizations, dual-polarized antennas can effectively utilize the available spectrum more efficiently. This is particularly useful in crowded frequency bands where there is limited spectrum available.

4. Simplified installation: Dual-polarized antennas can be installed in a single unit, reducing the complexity and cost of installation. This is especially advantageous in situations where space is limited or when deploying a large number of antennas.
5. Future-proofing: As data demand continues to grow, dual-polarized antennas provide a future-proof solution by increasing the capacity of the network without the need for additional infrastructure or equipment upgrades.
Overall, dual-polarized antennas are essential for networks that require high capacity, reliable connections, and efficient spectrum utilization. They are a cost-effective and practical solution to meet the ever-increasing demand for data transmission.
What is the Difference Between Single and Dual Polarized Antennas?
Single-polarized antennas are designed to transmit and receive signals in only one polarization, either horizontal or vertical. This means that they can only transmit or receive signals that are polarized in the same direction. If the polarization of the signal does not match that of the antenna, there will be a significant loss of signal strength.
On the other hand, dual-polarized antennas are capable of transmitting and receiving signals in two polarizations, both horizontal and vertical. This allows them to communicate with devices that have different polarization orientations. Dual-polarized antennas provide a more reliable and efficient communication channel because they can adapt to the polarization of the incoming signal, resulting in stronger and clearer signals.

In summary, the main difference between single and dual-polarized antennas is that single-polarized antennas operate on one polarization, while dual-polarized antennas operate on both horizontal and vertical polarizations, providing a more versatile and effective means of signal transmission.
What are the Different Types of Polarity?
1. Horizontal Polarity: In horizontal polarization, the electric field is aligned parallel to the ground. This type of polarization is commonly used in television broadcasting and satellite communication.

2. Vertical Polarity: In vertical polarization, the electric field is aligned perpendicular to the ground. This type of polarization is also commonly used in wireless communication, television broadcasting and satellite communication.

3. Circular Polarity: In circular polarization, the electric field rotates in a circular pattern as the wave propagates. Circular polarization can be further divided into two subtypes: right-hand circular polarization (RHCP) and left-hand circular polarization (LHCP). Circular polarization is commonly used in satellite communication, GPS systems, RFID and wireless communication.
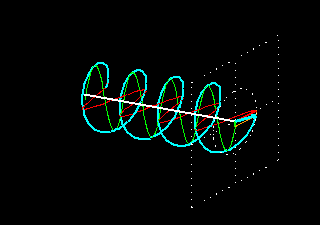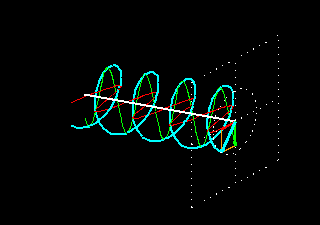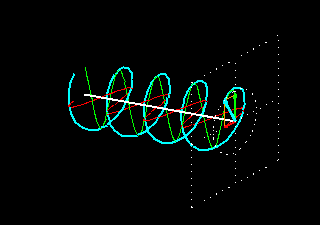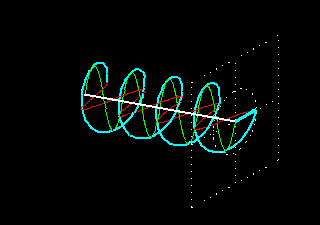
4. Slant Polarity: Slant 45 polarization is a type of polarization used in mobile communication. It refers to the orientation of the electric field of a radio wave in relation to the Earth’s surface. In slant 45 polarization, the electric field is oriented at a 45-degree angle to the Earth’s surface. This type of polarization is commonly used in cellular networks to minimize signal interference and improve signal quality.

It is important to note that the choice of polarization depends on various factors such as the type of communication system, the distance between the transmitter and receiver, the presence of obstacles, and the desired signal quality.
How Does Transmission Frequency Impact Polarization?
Transmission frequency plays a significant role in determining how polarization behaves in a wireless communication system. As the frequency of a signal increases, so does its sensitivity to changes in polarization.
At higher frequencies—commonly used in microwave, satellite, and cellular networks—signals are much more susceptible to polarization mismatches. Even slight misalignments between transmitting and receiving antennas can lead to a significant drop in signal strength. This greater sensitivity is due to the fact that higher frequency waves interact more readily with physical obstacles, such as buildings, trees, or even atmospheric moisture, which can alter the polarization as the signal propagates.
In lower-frequency applications, like traditional FM radio or some TV broadcasting, polarization is less affected by minor shifts in orientation or obstacles in the environment. However, as you move up the spectrum into frequencies used by modern 5G networks or satellite links, careful alignment of antenna polarization becomes increasingly important to maintain a clear, strong signal.
To sum up, higher transmission frequencies require more precise polarization alignment and are more likely to experience polarization changes caused by the environment. This is one reason why advanced antenna designs—such as dual-polarized or circularly polarized antennas—are often used at higher frequencies, to ensure more reliable signal quality despite these challenges.
What is Dual Circular Polarization and Where is it Used?
Dual circular polarization is a specialized form of antenna polarization where both right-hand circular polarization (RHCP) and left-hand circular polarization (LHCP) are utilized, either simultaneously or selectively. In circular polarization, the electric field of the electromagnetic wave rotates in a circular motion as it propagates, rather than oscillating in a straight line (linear polarization) or tracing an ellipse (elliptical polarization). Dual circular polarization involves the capability to transmit and receive signals with both senses of circular polarization, providing additional flexibility and performance benefits.
This type of polarization is widely used in satellite communications, radar systems, and wireless communication links. Dual circular polarization is particularly valuable in applications where signals may encounter multipath reflections, atmospheric effects, or orientation changes between the transmitter and receiver. By supporting both RHCP and LHCP, systems can minimize interference, improve signal isolation, and allow for the simultaneous transmission of independent data streams on the same frequency (a technique known as polarization diversity or polarization multiplexing).
In summary, dual circular polarization enhances communication reliability and bandwidth efficiency, making it a preferred choice in advanced satellite, radar, and wireless systems where robust and flexible signal transmission is essential.
H+V Dual Polarity Antenna vs +/- 45 Dual Slant Polarized Antenna
The H+V Dual Polarity Antenna and the +/- 45 Dual Slant Polarized Antenna are two different types of antennas used in wireless communication systems.

- This type of antenna has two separate radiating elements, one for horizontal polarization (H) and one for vertical polarization (V).
- It can transmit and receive signals in both horizontal and vertical polarizations simultaneously.
- It is typically used in applications where the polarization of the incoming signals can vary or is unknown.
- It provides better diversity in signal reception, which can help improve the overall performance and reliability of the wireless system.
- It requires two separate feedlines or connectors to connect to the radio equipment.
H+V Polarization Diversity Benefits
In addition, H+V dual polarity antennas are a key component in implementing polarization diversity—a technique where multiple versions of a signal are transmitted and received using different types of polarization. This approach helps mitigate polarization mismatch, ensuring that the signal is received even if its polarization changes during propagation. Polarization diversity also helps reduce signal degradation caused by multipath interference, which is especially common in complex environments like urban areas.
This technique is particularly valuable in MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output) systems, where it enables improved performance without the need for as many separate antennas. By using signals with low correlation between their polarizations, MIMO systems can achieve higher reliability and data throughput. However, it’s worth noting that while polarization diversity offers significant advantages, it can also increase system complexity and cost due to the additional hardware required.
- It requires two separate feedlines or connectors to connect to the radio equipment.
- It requires two separate feedlines or connectors to connect to the radio equipment.
2. +/- 45 Dual Slant Polarized Antenna:


- This type of antenna has two radiating elements that are oriented at +/- 45 degrees with respect to the horizontal plane.
- It transmits and receives signals with two different slant polarizations, typically referred to as +45 and -45 degrees.
- It is used in applications where the polarization of the incoming signals is known and fixed, such as point-to-point microwave links.
- It provides better isolation between adjacent antennas and reduces the interference caused by cross-polarization.
- It requires only one feedline or connector to connect to the radio equipment.
In summary, the H+V Dual Polarity Antenna is suitable for applications where the polarization of the signals is unknown or can vary, while the +/- 45 Dual Slant Polarized Antenna is used in applications where the polarization of the signals is known and fixed.
Which Type of Polarity is Commonly Used?
For example, horizontal polarization is often used in broadcast television because it provides a good balance between coverage and interference rejection. It is also commonly used for satellite communication because it minimizes the effects of rain fade.
Vertical polarization, on the other hand, is often used in mobile communication because it provides better coverage in urban environments where buildings can cause signal blockage. It is also commonly used for radar systems because it provides better detection of targets at low altitudes.
In some cases, circular polarization may be used instead of horizontal or vertical polarization. Circular polarization is often used in RFID communication and IoT system because it allows for better signal reception regardless of the orientation. It is also commonly used in wireless communication systems because it provides better resistance to multipath fading.

In summary, the choice of polarization depends on various factors including the application, environment, and specific system needs. Horizontal and vertical polarizations are commonly used due to their simplicity and effectiveness, but circular polarization may be used in certain cases.
Types of Linear Polarization
Linear polarization is the most common form used in practical wireless applications. In this type, the electric field (E-field) oscillates in a single plane. Depending on the orientation of this oscillation, linear polarization can be divided into:
- Horizontal polarization: The E-field oscillates from side to side, ideal for applications like television broadcasting and certain satellite links.
- Vertical polarization: The E-field oscillates up and down, making it well-suited for mobile communications and radar systems.
- Slant polarization: The E-field oscillates at an angle (such as +45° or -45°) rather than purely horizontal or vertical. This approach is frequently used to improve signal diversity and reduce interference, especially in systems where both horizontal and vertical polarizations might be present.
By choosing the appropriate polarization—horizontal, vertical, or slant—engineers can optimize system performance for specific environments and applications.
In some cases, circular polarization may be used instead of horizontal or vertical polarization. Circular polarization is often used in RFID communication and IoT systems because it allows for better signal reception regardless of the orientation. It is also commonly used in wireless communication systems because it provides better resistance to multipath fading.
Additionally, circular and elliptical polarizations are widely adopted in satellite and radar systems due to their ability to handle the high degree of interference present in these environments. For satellite communication, circular polarization can effectively compensate for signal distortion caused by the rotation or movement of satellites. In radio astronomy, both circular and elliptical polarizations are utilized to study the motion of large celestial bodies, offering unique advantages when analyzing signals affected by dynamic orientations or propagation conditions.
In summary, the choice of polarization depends on various factors including the application, environment, and specific system needs. Horizontal and vertical polarizations are commonly used due to their simplicity and effectiveness, but circular polarization may be used in certain cases.
Which Polarization is Best for an Antenna?
The best polarization for an antenna is determined by the intended use case. Factors to consider include the operating environment, the type of data being transmitted, and the presence of obstacles that might affect signal propagation.
For example, in a line-of-sight communication scenario, where the transmitting and receiving antennas have a clear, unobstructed view of each other, vertical polarization is often used. This is because the majority of man-made and natural obstacles, such as buildings and trees, have horizontal polarization characteristics. By using vertical polarization, the antenna can minimize the interference caused by these obstacles.

On the other hand, if the communication is happening in an environment with a lot of reflections, such as in a city with tall buildings, horizontal polarization may be more suitable. This is because horizontal polarization tends to have better penetration through walls and other obstacles, while vertical polarization may suffer from signal cancellation due to reflections.
In some cases, circular polarization may be used to achieve a combination of both vertical and horizontal polarization characteristics. Circular polarization is less affected by the orientation of the receiving antenna, making it suitable for situations where the antenna may be moving or where the relative orientation between the transmitting and receiving antennas is not fixed.
Practical Considerations for Choosing Antenna Polarization
While the above guidelines cover common scenarios, it’s important to take into account a few practical considerations:
- Proper alignment and orientation: The effectiveness of an antenna’s polarization relies heavily on how well the transmitting and receiving antennas are aligned. Even a slight misalignment can significantly degrade signal strength and clarity—especially in directional links, where precision matters.
- Mitigating polarization mismatch: Polarization mismatch between antennas can weaken or even prevent successful signal reception. To address this challenge, techniques like polarization diversity (using multiple polarizations simultaneously) and adaptive polarization (dynamically adjusting to match conditions) can be employed.
- Antenna selection criteria: The choice of antenna should reflect both the desired polarization and the application. For instance, hand-held mobile radios generally utilize vertically polarized dipole antennas for optimal performance. Wire antennas are often chosen for high-frequency bands, while linear polarization is prevalent at higher frequencies for specific communication needs.
In summary, the best polarization for an antenna depends on the specific use case and the factors mentioned above. It is important to consider the operating environment, the type of data being transmitted, and the presence of obstacles in order to determine the most appropriate polarization.

Does Antenna Polarization Matter?
Yes, antenna polarization does matter. The polarization of an antenna refers to the orientation of the electromagnetic waves it emits or receives. There are two main types of antenna polarization: vertical and horizontal.
The polarization of an antenna must match the polarization of the signal being transmitted or received for optimal performance. When the polarizations are aligned, the signal can be efficiently transmitted or received, resulting in better signal strength and quality.
If the polarizations are misaligned, the signal can be weakened or even completely blocked. This is because when the polarizations are perpendicular to each other, the signal experiences a phenomenon called polarization loss. This loss occurs because the electric field of the signal cannot effectively couple with the antenna, leading to reduced signal strength and potentially poor communication performance.
Mitigating Polarization Mismatch
Polarization mismatch can eventually cause failure in the reception of the correct signal. To address this, techniques such as polarization diversity and adaptive polarization are often used. Polarization diversity involves using multiple antennas with different polarizations to improve the chances of a strong signal, while adaptive polarization systems can adjust the polarization dynamically to match changing conditions. These approaches help maintain reliable communication even in environments with varying or unpredictable signal orientations.
In addition to alignment, antenna polarization also affects signal penetration and system efficiency. For example, vertical polarization is often used for ground-to-air communication because it provides better signal penetration through obstacles such as buildings or trees. On the other hand, horizontal polarization is often used for point-to-point communication because it minimizes interference from other signals with different polarizations.
Overall, antenna polarization is a critical consideration in system design to ensure optimal performance, signal clarity, penetration, and system efficiency.
The Impact of Adaptive Polarization and Machine Learning on Antenna Technology
Recent advancements in wireless technologies, especially with the arrival of 5G and the anticipated rollout of 6G, have brought adaptive polarization techniques and machine learning to the forefront of antenna innovation.

Adaptive polarization allows antennas to dynamically adjust their polarization state in real time to suit changing environments and signal conditions. This adaptability enhances signal quality by minimizing polarization mismatch and maximizing the efficiency of data transmission. In environments prone to interference—such as urban centers crowded with tall buildings or areas with multiple signal sources—adaptive polarization can significantly improve both reliability and throughput.
Machine learning is also transforming antenna technology. By analyzing past signal patterns and environmental conditions, machine learning algorithms can predict optimal antenna configurations and adapt system parameters on the fly. This intelligence helps networks automatically respond to challenges like signal fading, physical obstructions, and varying device orientations without human intervention.
What’s more, these advances are crucial for emerging applications such as Internet of Things (IoT) networks, drone communications, and connected vehicle systems. For instance, intelligent reflective surfaces—another developing technology—use smart algorithms to steer and shape radio waves for even more efficient wireless coverage.
In summary, adaptive polarization and machine learning are not just buzzwords; they are fundamentally reshaping how antennas operate, providing smarter, more resilient, and efficient communication systems.
What Are the Future Trends and Developments in Antenna Polarization Technology?
Looking ahead, antenna polarization technology is set to play a pivotal role in shaping the next generation of wireless communication. With the rollout of 5G networks and the oncoming wave of 6G development, researchers and engineers are actively exploring new frontiers that promise even greater efficiency and adaptability.
A few notable trends are emerging on the horizon:
- Adaptive Polarization Systems: Modern wireless networks are increasingly experimenting with antenna systems capable of dynamically switching polarization modes. This adaptability helps maintain strong connections, even in environments where signal conditions rapidly change—an essential advancement for urban infrastructure and mobile applications.
- Machine Learning Integration: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are making their mark by optimizing how antennas choose and shift polarization. These smart algorithms can analyze signal environments in real time, automatically adjusting parameters to maximize signal quality and network performance.
- Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRS): Pioneering work is underway on using intelligent reflective surfaces—panels that can redirect and manipulate electromagnetic waves to improve signal strength and coverage. By customizing the polarization properties of these surfaces, engineers can further reduce interference and boost data throughput.
- Support for New Applications: Enhanced polarization technology is critical for emerging fields such as the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and drone communication systems. These applications demand reliable, interference-resistant links—challenges well-suited to the next generation of dual and adaptive polarization systems.
In short, the future of antenna polarization is being shaped by a blend of smarter algorithms, dynamically responsive hardware, and groundbreaking applications in everyday technology. As these trends continue, we can expect wireless communication to become not just faster, but more resilient and versatile across a wide range of environments.
Summary
Dual polarization antennas are a significant advancement in communication technology, providing improved performance, reliability, and efficiency. It is crucial for professionals in the tech industry to grasp the impact of antenna polarization to navigate the complexities of modern communication systems.
As we navigate the complexities of wireless communication, the role of dual polarization antennas becomes increasingly crucial. Their ability to double communication capacity without additional resources marks a significant leap forward, promising a future where data transmission is faster, more reliable, and more efficient than ever before.

